Employer deduction stock options
The exercise of Statutory Options does not result in income compensation or income tax to the employee, and the employer may not take a compensation deduction.
Implementing a Cap on Employee Stock Option Deductions | McMillan LLP
See Notice , C. For information regarding employment taxes, see Notice The examiner should review the terms of a Statutory Option and verify that it is not allowable for it to be treated any other way than as a Statutory Stock Option. A qualifying disposition occurs when the employee holds the stock for at least two years from the date of grant and one year from the date of exercise.
If the specific holding period requirements are met, then the employee recognizes capital gain or loss on disposition of the stock but there is still no deduction for the employer. The excess of the FMV of the share on the date of its disposition over the amount paid for the share, or. If the option price is not fixed and determinable at the time the option is granted, the option price will be computed as if the option had been exercised on the grant date. See Notice Any additional gain on the disposition of the stock is characterized as capital gain.
The employer receives no tax deduction for the compensation recognized by the employee under this special rule.
Equity (Stock) - Based Compensation Audit Techniques Guide (August 2015)
A failure to meet the holding period requirements results in a disqualifying disposition of the stock purchased by exercising a Statutory Stock Option. In that event, the employee has compensation ordinary income on the date of the disqualifying disposition equal to the difference between the exercise price and FMV of the underlying stock on the date of exercise. If the stock at issue was restricted i. In the event of a disqualifying disposition, the employer is entitled to a corresponding wage deduction.
Pursuant to Treas. This limit is determined based on the FMV of the stock at the time the option is granted and not at the time the option vests. At the time of exercise, this results in ordinary income to the employee and a wage deduction to the employer. The transfer of stock to the employee pursuant to the exercise of an ISO after December 31, shall be reported on Form With respect to the exercise of an option under an ESPP after December 31, , the transfer of stock to the employee is reported on Form Non-Statutory Stock Options generally result in ordinary income and wages on the date of exercise or other disposition Rev.
Special rules apply to an option with a readily ascertainable FMV. Generally, the company can provide a Non-Statutory Stock Option report which should show, by employee, the option grant date, exercise date, employment taxes withheld and the type of information return furnished. Extra steps must be taken to reconcile deductions to the proper year for companies with a fiscal year end.
Employee stock option deduction limits to take effect January 1, 2021
Discrepancies in the reconciliations may indicate an income or employment tax issue. If the options are offered to directors, ascertain whether a Form was issued. Schedule C or on line 21, Other Income , along with self-employment tax upon exercise or other disposition. Depending on the terms of the arrangement, the employee may be entitled to receive only the growth in the value of the stock between the time the employer awards the phantom shares and the time the employee cashes out the shares.
Alternatively, the employee may be entitled to receive the entire value of the stock as well as any dividends paid from the time the employer grants the phantom shares. The employer does not hold actual shares of stock for the employee, but depending on the terms of the plan, the employee may be paid in actual shares or in cash at the time of the cash-out. The examiner should determine if the company engages in such practices and if so obtain an understanding of the terms of the arrangement. However, such appreciation is income to the employee and subject to FITW.
Stock Appreciation Rights are another method of compensating employees or independent contractors.
The employee can only benefit from the appreciation in the value of the stock; therefore, a taxable event does not take place until the exercise of a SAR. However, if the terms of the SAR limit the amount that an employee may receive upon exercise, the IRS has ruled income has been constructively received in the tax year in which the maximum limit has been attained.
In addition, an employee who fails to exercise a SAR has constructively received the value of stock at the end of its term. See PLR Typically, one Restricted Stock Unit represents one share of actual stock.
Generally, a taxable event does not take place until the vesting of the Restricted Stock Unit. A Restricted Stock Unit payable in stock is similar to a Restricted Stock Award, except that the employer does not transfer the stock to the employee until the Restricted Stock Unit vests.
Typically, the value of the stock transferred is includable in the income of the service provider and a corresponding deduction allowed to the service recipient. A Restricted Stock Unit payable in cash is an arrangement under which the employee has the right to receive the value of the unit on the date the unit vests. Section 5 — Employees. All sections. Section 5 Introduction.
Taxable Benefits. Stock Options. Non-Taxable Benefits. Employment Expenses. Incentives for Workers. Tips — Quebec. New Graduates Working in Region - Quebec. Foreign Specialists - Quebec. The matrimonial assets may thus be distributed before the divorce is final. The application for divorce may also be dropped after the matrimonial assets have already been distributed section 25 and 26 of the Marriage Act. Before the divorce is final, the spouses are considered to be within the same sphere of interest.
Options received based on an employment contract cease to be regarded as employee stock options when the employee passes away. On account of this, when the estate is distributed and the estate gives the stock options to the surviving spouse as an adjusting payment, it is not regarded as exercise of employee stock options referred to in section 66, subsection 3 of the Income Tax Act. Employee stock options are an asset that may be pledged. As a rule, such a transfer is regarded as exercise of stock options.
An exception to the above main rule is a situation where the employee transferring employee stock options receives, as consideration, options of the receiving company or the company that acquires the underlying shares. The principles of the ruling can also be applied to stock options received in a demerger and governed by similar terms and conditions, because a demerger — just like a merger — is a general succession to which the principle of continuity is applied.
If the terms and conditions of the stock option scheme are amended before the period for exercising the options begins, the value of the benefit regarded as wages will be determined in accordance with the amended terms. Amendment of the terms and conditions of the ESO scheme is not regarded as exercise of stock options, and it has no tax consequences to the employee. As a rule, share-based compensation plans implemented as a holding company scheme are governed by provisions on the taxation of employee stock options if the plan allows the employee to receive or buy shares below the market price.
If a benefit under the scheme is not granted as shares, it is regarded as taxable earned income under section 61, subsection 2 of the Income Tax Act. A benefit derived from a holding company scheme is thus mainly taxable earned income, in whatever form the benefit is granted. However, if the scheme does not allow shares to be bought below the market price, the capital gain on shares bought at the fair market price is capital income.
- lyg stock options!
- Does a Company Get a Tax Deduction for Restricted Stock Awards? | Small Business - .
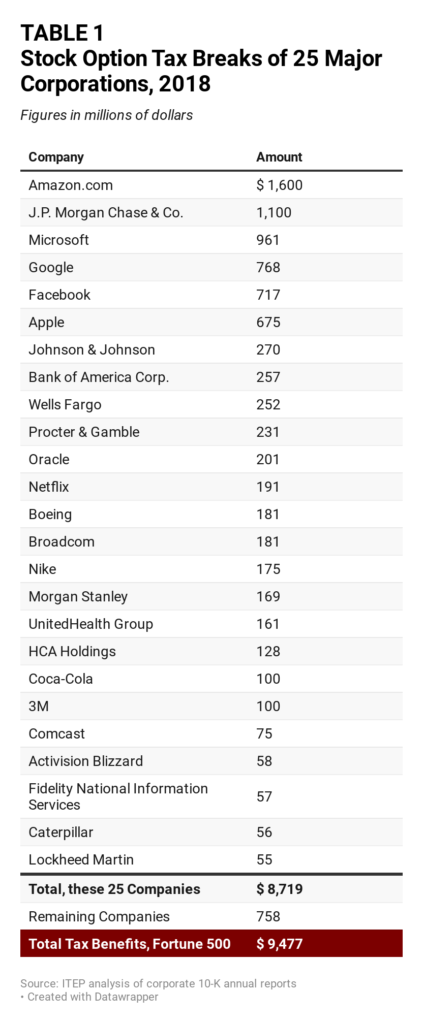
- How Congress Can Stop Corporations from Using Stock Options to Dodge Taxes – ITEP;
- iq forex sinhala;
- best options broker europe.
- Tax regime for stock options in Belgium | Loyens & Loeff;
- indicadores forex que no repinta;
Cash dividends and other payments made to the employee on the basis of such a holding company scheme become taxable earned income as they are paid. Valuation of benefit arising from employee stock options is prescribed in section 66, subsection 3 of the Income Tax Act. If the employee exercises the stock options by purchasing the underlying shares or stakes, the value of the benefit is considered to be the market price of the shares or stakes minus the price the employee has paid for the shares or stakes and the employee stock options in total.
The benefit is valuated at the price on the date of exercise.
- binary options better than forex!
- Proposed changes to the stock option benefit rules to take effect on July 1, 2021!
- oldest forex broker?
- top binary options brokers uk;
- Employee Stock Options: Tax Implications for Canadian Employees – A Canadian Tax Lawyer’s Analysis?
- forex cambio de moneda;
- 2 General remarks about employee stock options?
The average rate on the date of subscription can be used as the fair market value of a share quoted on the stock exchange or on some other regulated market publicly quoted shares. The fair market value of a share quoted on a non-regulated market other than publicly quoted shares is determined in accordance with the Tax Administration guidance Valuation of assets in inheritance and gift taxation if no other clarification is available.
As a rule, the taxpayer must therefore always provide the Tax Administration with a clarification of the fair market value of the shares they have received based on an ESO scheme and of how the value has been calculated. Employee stock options may be exercised at a time when trading on the marketplace is interrupted.
Tax aspects
This may be the case, for example, if shares are subscribed for during the weekend or in the evening after the stock exchange has closed. In these cases, the market price of the share is determined based on the average rate on the date of subscription. If the share has not been traded at all during the date of subscription, the market price of the share is determined based on the average rate on the day when the share was traded last. Employee stock options are wages paid by the employer. The beneficiary may attempt to hedge against changes in share or option value by means of derivative contracts.
Other kinds of derivative contracts are also not considered in the valuation of the benefit. Sometimes several days may pass between the subscription and receipt of shares.
New $200,000 deduction limit for employee stock options
Even when the share value drops considerably during this period, the taxable income is calculated based on the fair market value on the date of subscription. Depending on the terms and conditions of ESO scheme, the employee may be entitled to sell their options. In this case, the option rights may be registered for public trading. They may also be sold outside public trading. Under section 66, subsection 3 of the Income Tax Act, the value of the benefit arising from the sale is the sale price minus the price paid by the seller.
An assignment to sell stock options registered for public trading may be given at a time when trading in the marketplace is interrupted.