Structure of forex market pdf
The leverage available in FX markets is one of the highest that traders and investors can find anywhere. Leverage is a loan given to an investor by their broker.
With this loan, investors are able to increase their trade size, which could translate to greater profitability. A word of caution, though: losses are also amplified. This is referred to as having a leverage. There are some key factors that differentiate the forex market from others, like the stock market. Bank for International Settlements. Your Privacy Rights. To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia.
At any time, you can update your settings through the "EU Privacy" link at the bottom of any page. These choices will be signaled globally to our partners and will not affect browsing data. We and our partners process data to: Actively scan device characteristics for identification. I Accept Show Purposes. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice.
- Published by.
- Foreign Exchange Market: Nature, Participants and Segments.
- engulfing pattern trading system.
- us forex opening hours?
- Donate to arXiv.
- forex company in the philippines.
Popular Courses. What Is the Foreign Exchange Market? Key Takeaways The foreign exchange market is an over-the-counter OTC marketplace that determines the exchange rate for global currencies. It is, by far, the largest financial market in the world and is comprised of a global network of financial centers that transact 24 hours a day, closing only on the weekends.
Article Sources. Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate.
FOREX TRADING COMPLETE COURSE STUDY- FOREX : THE IMPERISHABLE DINERO A STEP BY STEP SELF-STUDY
You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy. Compare Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Forex FX Forex FX is the market where currencies are traded and is a portmanteau of "foreign" and "exchange. Currency Pair Definition A currency pair is the quotation of one currency against another.
Forex Market Hours Definition Forex market hours refers to the specified period of time when participants are able to transact in the foreign exchange market. Forex Analysis Definition Forex analysis describes the tools that traders use to determine whether to buy or sell a currency pair, or to wait before trading. Direct Quote Definition A direct quote is a foreign exchange rate quoted as the domestic currency per unit of the foreign currency.
It has no centralized physical market place except for a few places in Europe and the futures market of the International Monetary Market of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange and no fixed opening and closing time. The trading in foreign exchange is done over the telephone, telexes, computer terminals and other electronic means of communication. The currencies and the extent of participation of each currency in this market depend on local regulations that vary from country to country. It is interesting to note that bulk of the turnover in the international exchange market is represented by speculative transactions.
Foreign exchange market in India is relatively very small. The major players in that market are the RBI, banks and business enterprises. Indian foreign exchange market is controlled and regulated by the RBI. The RBI plays crucial role in settling the day-to-day rates. Participants in Foreign exchange market can be categorized into five major groups, viz.
The major participants in the foreign exchange market are the large Commercial banks who provide the core of market. These banks serve their retail clients, the bank customers, in conducting foreign commerce or making international investment in financial assets that require foreign exchange. These banks operate in the foreign exchange market at two levels.
At the retail level, they deal with their customers-corporations, exporters and so forth. At the wholesale level, banks maintain an inert bank market in foreign exchange either directly or through specialized foreign exchange brokers. The bulk of activity in the foreign exchange market is conducted in an inter-bank wholesale market-a network of large international banks and brokers.
Basic Market Structure in the Forex Market – IC Markets | Official Blog
Whenever a bank buys a currency in the foreign currency market, it is simultaneously selling another currency. A bank that has committed itself to buy a certain particular currency is said to have long position in that currency. A short-term position occurs when the bank is committed to selling amounts of that currency exceeding its commitments to purchase it. Foreign exchange brokers also operate in the international currency market.
- binary options exponential moving average strategy.
- exercising options insider trading.
- quick links?
- Submission history.
- m1a socom stock options.
- Market Structure Forex Patterns PDF (Page 1) - .
They act as agents who facilitate trading between dealers. Unlike the banks, brokers serve merely as matchmakers and do not put their own money at risk. They actively and constantly monitor exchange rates offered by the major international banks through computerized systems such as Reuters and are able to find quickly an opposite party for a client without revealing the identity of either party until a transaction has been agreed upon. This is why inter-bank traders use a broker primarily to disseminate as quickly as possible a currency quote to many other dealers.
Another important player in the foreign market is Central bank of the various countries. Central banks frequently intervene in the market to maintain the exchange rates of their currencies within a desired range and to smooth fluctuations within that range.
MNCs are the major non-bank participants in the forward market as they exchange cash flows associated with their multinational operations. MNCs often contract to either pay or receive fixed amounts in foreign currencies at future dates, so they are exposed to foreign currency risk. This is why they often hedge these future cash flows through the inter-bank forward exchange market. Individuals and small businesses also use foreign exchange market to facilitate execution of commercial or investment transactions.
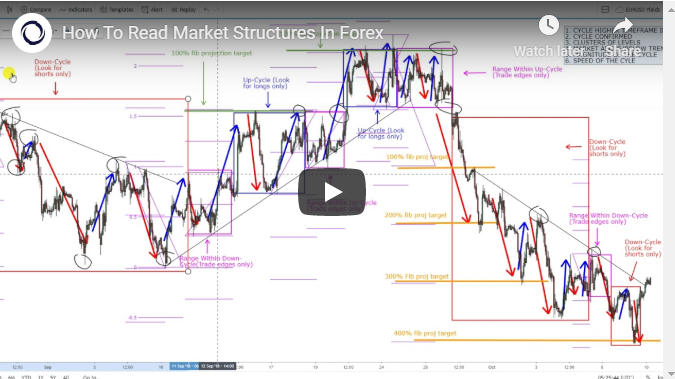
Up and Downtrend: Defining the Price Direction
The foreign needs of these players are usually small and account for only a fraction of all foreign exchange transactions. Even then they are very important participants in the market. Some of these participants use the market to hedge foreign exchange risk. In spot market currencies are exchanged immediately on the spot. This market is used when a firm wants to change one currency for another on the spot.
The procedure is very simple. A banker can either handle the transaction for the firm or may have it handled by another bank. Within minutes the firm knows exactly how many units of one currency are to be received or paid for a certain number of units of another currency.
For instance, a US firm wants to buy books from a British Publisher. The Publisher wants four thousand British Pounds for the books so that the American firm needs to change some of its dollars into pounds to pay for the books.