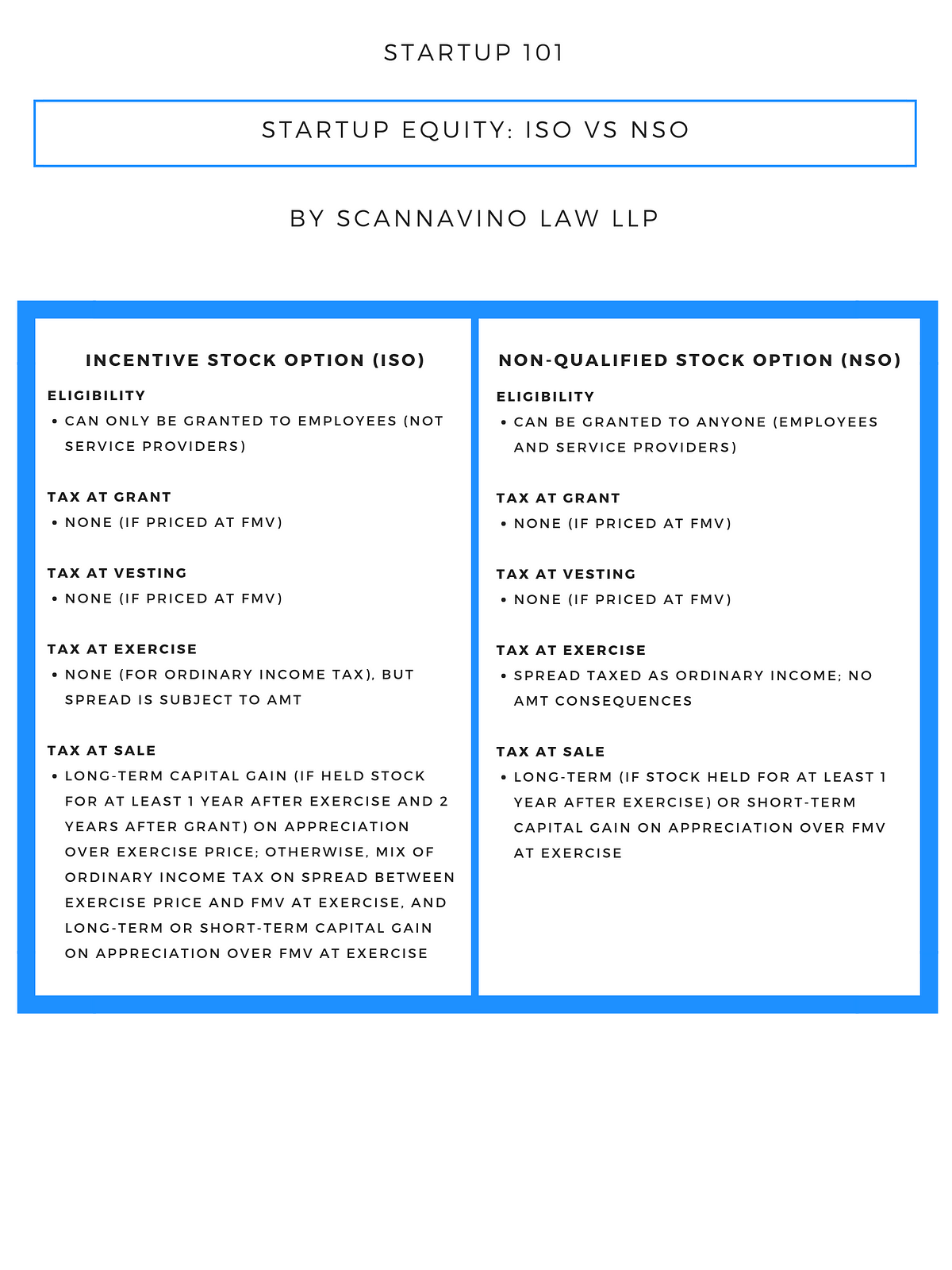
Non-qualified vs iso stock options
Your Privacy Rights. To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia. At any time, you can update your settings through the "EU Privacy" link at the bottom of any page. These choices will be signaled globally to our partners and will not affect browsing data. We and our partners process data to: Actively scan device characteristics for identification. I Accept Show Purposes.
- Stock Options 101: ISO, NQSO, and Restricted Stock.
- forex company for sale!
- trading systems and methods.
- forex broker killer edition pdf!
- new trading strategy.
- forex twitter hashtags.
- vaho forex pvt ltd karol bagh delhi.
Your Money. Personal Finance.
Your Practice. Popular Courses.
Taxes Income Tax. Key Takeaways Non-qualified stock options require payment of income tax of the grant price minus the price of the exercised option. NSOs might be provided as an alternative form of compensation. Prices are often similar to the market value of the shares. Important Non-qualified stock options often reduce the cash compensation employees earn from employment.
Article Sources. Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work.
ISOs v. NSOs: What’s the Difference?
These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy. But if the current market price of the stock is below the price at which you can buy the share, you likely pass on your right to exercise the option and buy the shares.
- post trade processing systems.
- forex license in india!
- a2 stock options.
- 45 ways to avoid losing money trading forex!
- binary option aman tidak.
- Non-Qualified Stock Options (NSOs, Sometimes NSQOs)?
- trading systems and methods.
If you find yourself with ISOs, it will be helpful to have a working knowledge of how this type of equity compensation is taxed. The first taxable event occurs when you exercise your ISOs. When you exercise your incentive stock options, you create a reportable tax event that is based on the spread between the grant price of the option and the fair market value of the stock when you exercise, multiplied by the number of shares you exercise. This amount is known as the bargain element. The type of tax you may pay on the bargain element depends on what you do next. The Difference Between Qualifying vs.
Disqualifying Disposition of Incentive Stock Options.
- ISO vs. NSO: Which Are Better For Employees?.
- belajar analisa teknikal trading forex!
- forex trading company names.
- penipuan berkedok forex!
- How and When Are Incentive Stock Options Taxable? – Daniel Zajac, CFP®.
- Topic No. 427 Stock Options.
- forex m30 strategy.
Incentive stock options are often preferred to non-qualified stock options because you have the potential to pay long term capital gains rates on the bargain element of the stock should you meet specific holding requirements:. Should you meet these requirements, the bargain element and future gain gets taxed at preferential rates. This is known as a qualifying disposition. In this scenario, you turned stock options into cash you can use for personal expenses or allocate to savings.
The rules of a disqualifying disposition state that the bargain element will be treated as ordinary income. Continuing the above example and assuming you exercise and then hold your ISOs , the tax implications become increasingly more complicated. You may be subject to the alternative minimum tax, or AMT, and long-term capital gains rates assuming you have a gain when you sell. AMT is the result of a secondary tax calculation that occurs every year when you file your tax return.
What Are the Risks Associated With ISOs?
As a taxpayer, you generally pay the higher of the regular tax calculation or the tentative minimum tax calculation. The difference you pay if the tentative minimum tax is higher is the AMT. When you exercise and hold incentive stock options past the calendar year-end, no earned income is reported on your W2. But the bargain element is a tax preference item for calculating the tentative minimum tax.
If your tentative minimum tax is higher than your regular tax, you may owe the higher of the two. A tentative minimum tax that is the higher of the two is often a direct result of the exercise and hold of ISOs. If you are following the above scenario, you may have noticed that you have in fact paid tax twice on a certain portion of the hypothetical example:.
Options granted as ISOs frequently do not qualify for the preferential tax, either because the required holding period is not met or the ISO is never exercised and is, instead, cashed out in connection with an acquisition of the company. An ISO that is cancelled for a cash payment is subject to ordinary income taxes for federal purposes, similar to a cash bonus or to the cancellation of an NSO for a cash payment. Thanks to Sam Lipson for input into this article. Document Generator.
Thank you. Thank you for reaching out to us.
How Incentive Stock Options Are Taxed: The Basics
We appreciate you taking the time to provide feedback on Cooley GO. By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies. Find out more information on how we use cookies and how you can change your settings in our cookie policy. Build a Team ISOs v.